How are Lithium-ion Batteries Recycled?

Lithium-ion batteries are integral to modern technology, powering everything from smartphones and laptops to electric vehicles and renewable energy storage systems. Their widespread use has led to an increasing need for effective recycling methods as these batteries reach the end of their life cycle.
Recycling lithium-ion batteries is crucial for reducing environmental impact, recovering valuable materials, and promoting sustainable practices. This blog will explore the lithium-ion battery recycling process, its benefits, challenges, and the future of battery recycling.
What Are Lithium-Ion Batteries?
Lithium-ion batteries are rechargeable energy storage devices that utilize lithium ions as the primary charge carriers. They consist of several battery components:
- Anode: Typically made from graphite, it stores lithium ions during charging.
- Cathode: Made from metal oxides (like lithium cobalt oxide or lithium iron phosphate), it releases lithium ions during discharge.
- Separator: A thin membrane that prevents direct contact between the electrodes i.e anode and cathode while allowing ions to pass through.
- Electrolyte: A liquid or gel that facilitates the movement of lithium ions between the anodes and cathodes.
These rechargeable batteries are favored for their high energy density, low self-discharge rates, and long cycle life compared to other battery types like lead-acid or nickel-metal hydride batteries.
What are Lithium-Ion Batteries Used For?
Lithium-ion batteries are used in various applications, including:
- Consumer Electronics: Smartphones, tablets, laptops, cameras, and wearable devices.
- Electric Vehicles (EVs): Powering electric cars, buses, and two-wheelers.
- Energy Storage Systems: Storing energy generated from renewable sources like solar and wind for later use.
As the demand for these applications grows, so does the need for sustainable approach and effective recycling methods to manage the waste generated by spent lithium-ion batteries.
Lithium Ion Battery Recycling Process: How is a Lithium Ion Battery Recycled?
The recycling process for lithium-ion batteries involves several critical steps:
1. Collection
The first step in recycling li-ion batteries is collection. Batteries can be collected from various sources:
- Retail Drop-off Points: Many retailers provide designated collection bins for used batteries.
- Municipal Recycling Programs: Local governments often organize collection events or provide drop-off locations for residents to dispose of their e-waste responsibly.
- Mail-in Programs: Some companies offer mail-in options where consumers can send their used batteries for recycling.
Proper handling during collection is crucial to prevent damage or short circuits that could pose safety hazards.
2. Sorting
After collection, lithium batteries are sorted based on their chemistry and physical characteristics. Sorting is essential because different types of batteries may contain varying compositions of metals and require different processing methods. Key factors considered during sorting include:
- Battery Chemistry: Identifying whether the battery contains cobalt-based cathodes or nickel-based ones affects how they will be processed.
- Condition of Batteries: Damaged or leaking batteries may require special handling due to safety concerns.
3. Preprocessing
Once sorted, the next step is preprocessing. This stage may involve several techniques:
- Mechanical Crushing – Mechanical crushing involves breaking down the batteries into smaller pieces using crushers and shredders. This process helps liberate components for further separation.
- Separation Techniques – After mechanical crushing, various separation techniques are employed to isolate different materials:
- Magnetic Separation: Used to extract ferrous metals from non-ferrous materials.
- Air Classification: Separates lighter materials from heavier ones based on density.
The goal is to produce a mixture known as “black mass,” which contains valuable metals such as lithium, cobalt, nickel, manganese, copper, and aluminum.
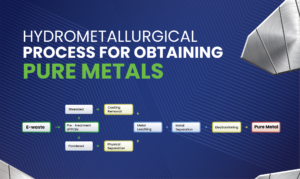
4. Hydrometallurgical Processing
Hydrometallurgy involves using chemical solutions to dissolve metals from black mass. Hydrometallurgical methods typically includes several steps:
1. Leaching: The black mass is treated with acids or other solvents that dissolve specific metals while leaving behind impurities.
2. Purification: The resulting solution undergoes purification processes such as precipitation or ion exchange to isolate desired metals.
3. Recovery: The purified metals are recovered through electrochemical processes or crystallization methods.
Hydrometallurgical processes are particularly effective for recovering high-value metals like cobalt and nickel while minimizing environmental impact compared to traditional mining practices.
5. Pyrometallurgical Processing
In some cases where hydrometallurgical processes may not be feasible or cost-effective—especially for low-value metals—pyrometallurgical processing may be employed:
1. Smelting: The crushed battery materials are subjected to high temperatures in a furnace where metals are melted down.
2. Separation: Different metals separate based on their melting points; this allows for recovery of various metal alloys.
While pyrometallurgy can recover certain metals effectively, it tends to be less environmentally friendly due to emissions produced during combustion processes.
6. Final Processing
After recovering valuable materials through either hydrometallurgical or pyrometallurgical methods —the final step involves refining these recovered metals into usable forms suitable for manufacturing new products:
- Metals may be cast into ingots or powders ready for reuse in battery production or other applications.
- Non-recyclable components (such as plastics) may undergo further processing or disposal according to environmental regulations.
Benefits of Recycling Lithium-Ion Batteries
Lithium battery recycling offers numerous benefits across environmental, economic, and social dimensions:
Environmental Benefits
1. Reduced Landfill Waste: Recycling prevents hazardous waste from ending up in landfills where it could leach harmful substances into soil and groundwater.
2. Conservation of Resources: By recovering valuable materials like lithium and cobalt through recycling rather than mining them anew—natural resources are conserved while reducing habitat destruction associated with extraction activities.
3. Lower Carbon Footprint: Recycling requires less energy than producing new materials from raw resources—leading to lower greenhouse gas emissions overall.
Economic Benefits
1. Material Recovery Savings: Companies can save costs by reusing recovered metals instead of purchasing new raw materials—creating a more sustainable supply chain overall.
2. Job Creation Opportunities: The growth of battery recycling facilities generates employment opportunities within local communities—contributing positively toward economic development efforts nationwide.
Social Benefits
1. Public Health Protection: Properly managing end-of-life lithium-ion batteries reduces risks associated with exposure to toxic chemicals found within them—protecting nearby communities’ health outcomes significantly over time.
2. Increased Consumer Awareness: Promoting responsible disposal practices encourages consumers to participate actively in sustainability initiatives—fostering a culture focused on environmental stewardship among individuals across society at large.
Challenges in Lithium-Ion Battery Recycling
Despite its importance, several challenges hinder effective lithium-ion battery recycling efforts:
1. Complexity of Battery Chemistry:
Different types of lithium-ion batteries have varying chemistries which complicate sorting processes; this requires specialized knowledge about each type’s composition before processing begins effectively.
2. Lack of Infrastructure:
Many regions lack adequate infrastructure needed for efficient collection systems—leading consumers unaware of proper disposal methods resulting in improper handling practices instead!
3. High Costs Associated with Recycling Technologies:
Advanced technologies required for efficient recovery processes often come at high initial investments—making it challenging financially viable without government support incentives!
4. Informal Sector Involvement
A significant portion of e-waste is managed by informal recyclers who may lack safety measures leading them potentially exposing workers & communities alike!
Future Trends in Lithium-Ion Battery Recycling
As technology continues evolving rapidly—several trends are emerging within the realm of lithium-ion battery recycling:
1. Advancements in Recycling Technologies
New technologies such as direct recycling methods aim at recovering active materials directly from spent cells without breaking them down entirely—promising higher recovery rates while reducing overall energy consumption during processing stages!
2. Circular Economy Initiatives
Emphasis on circular economy principles encourages manufacturers designing products with recyclability considerations integrated into their lifecycle management strategies—ensuring minimal waste generation throughout product use phases!
3. Regulatory Support
Governments worldwide increasingly recognize the importance of implementing regulations promoting responsible disposal practices—including extended producer responsibility (EPR) policies encouraging manufacturers’ accountability throughout their products’ lifecycles!
4. Consumer Education Efforts
Raising awareness about proper disposal options among consumers will play a crucial role in improving participation rates within existing programs aimed at facilitating effective end-of-life management solutions across industries!
Conclusion
The recycling of lithium-ion batteries is essential not only for reducing environmental impacts but also for recovering valuable resources needed to support ongoing technological advancements across battery recycling industry as well as multiple sectors—from consumer electronics through electric vehicles!
By understanding how recycling these batteries work—from collection through sorting & processing—we can better appreciate why prioritizing responsible disposal practices matters so much moving forward!
As demand for lithium-ion batteries continues to grow alongside increasing volumes generated annually—it becomes imperative we invest time & resources into developing efficient recycling techniques capable of meeting future challenges head-on! Through collaboration among stakeholders—including manufacturers consumers regulators alike—we can build a sustainable future where innovation thrives alongside environmental stewardship ensuring healthier ecosystems benefit all generations yet unborn!
FAQs
1. How can I recycle my old lithium-ion batteries?
To recycle old lithium-ion batteries, you can drop them off at designated collection points such as retail stores that offer battery recycling bins, municipal recycling programs, or special collection events. Some companies also provide mail-in recycling options where you can send your used batteries for proper disposal.
2. Can all lithium battery materials be recycled?
Yes, a significant portion of lithium-ion battery materials can be recycled. Research indicates that around 90% of the materials, including lithium, cobalt, and nickel, can be effectively recovered through various recycling processes. However, the efficiency may vary based on the battery chemistry and recycling technology used.